Improving indoor air quality is a critical concern for both residential and commercial environments. Air filters play a fundamental role in controlling airborne contaminants, ensuring healthier air, and protecting HVAC systems.
This article provides a detailed and technically accurate overview of different types of air filters, their efficiency ratings, selection criteria, 유지 보수 모범 사례.
What Are Air Filters and Why Are They Important?
Air filters are mechanical or electrostatic devices designed to remove particulate matter and, in some cases, gaseous pollutants from the air. They are essential components of heating, 통풍, 및 에어컨 (HVAC) systems, 공기 청정기, and specialized industrial equipment.
The primary function of an air filter is to trap airborne particles such as dust, 화분, 곰팡이 포자, 박테리아, 연기, 및 휘발성 유기 화합물 (voc). Removing these contaminants is vital not only for occupant health—reducing respiratory irritations, 알레르기, and exposure to pathogens—but also for maintaining the operational integrity of HVAC systems. Accumulated dust and debris can degrade system performance, increase energy consumption, and lead to costly repairs.
In environments with stringent air quality requirements, 병원과 같은, 실험실, and manufacturing cleanrooms, rail transportation, selecting the appropriate air filter is critical for compliance with health and safety standards.
에어 필터의 Merv 등급은 무엇입니까??
최소 효율성 보고 값 (Merv) is an industry-standard rating system developed by ASHRAE that quantifies a filter’s effectiveness at capturing airborne particles of various sizes. MERV 등급 범위는 다음과 같습니다. 1 에게 20, with higher numbers indicating higher filtration efficiency.
The following table summarizes the MERV rating ranges, the particle sizes they target, and typical applications:
| Merv 등급 범위 | Particle Size Range (미크론) | Example Particles | Filtration Efficiency and Typical Applications |
| 1-4 | 3.0 에게 10 | Dust, 화분, 카펫 섬유 | Basic filtration for large particles; common in residential window AC units |
| 5-8 | 1.0 에게 3.0 | Legionella bacteria, 먼지 진드기 잔해 | Suitable for standard residential and commercial buildings; captures smaller dust and mold spores |
| 9-12 | 0.3 에게 1.0 | 연기, aerosols, some viruses | High-efficiency filtration appropriate for hospitals and high-occupancy commercial spaces |
| 13-16 | 0.3 에게 1.0 | 박테리아, 연기 | Used in healthcare facilities and laboratories; capable of filtering bacteria and smoke |
| 17-20 | 0.3 and smaller | Microscopic particles including many viruses | HEPA and ULPA filters used in specialized cleanrooms; highest level of filtration |
또한 읽습니다: 에어 필터의 Merv 등급은 무엇입니까?? 당신이 알아야 할 모든 것
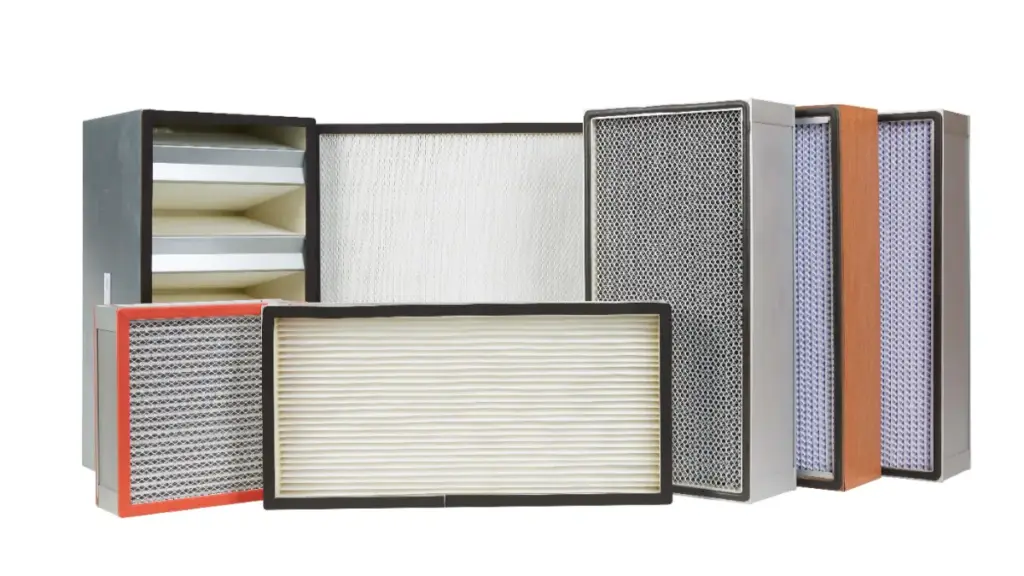
Common Types of Air Filters and Their Key Features
Air filters generally fall into three main categories: mechanical, electrostatic, and activated carbon filters, each addressing different pollutants and applications. Here is an overview of the most common types:
1. Fiberglass Filters

Fiberglass filters are the most basic type. They use layered fiberglass fibers to trap larger dust particles. They are inexpensive and provide minimal resistance to airflow, but their filtration efficiency is low, usually corresponding to MERV ratings of 1 에게 4. These filters are best for protecting HVAC systems but offer limited air quality improvement.
2. 주름 필터
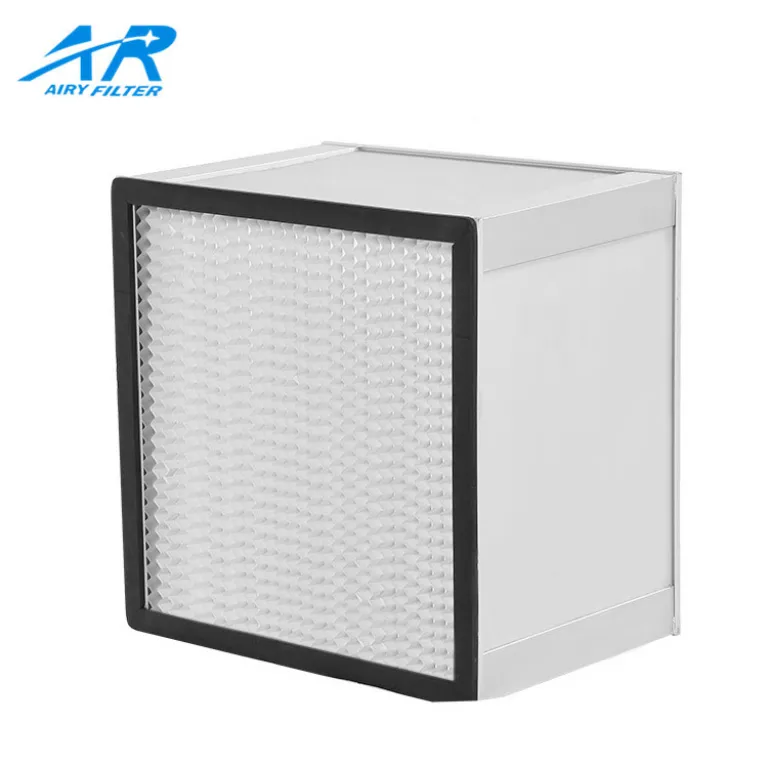

Pleated filters consist of folded fabric or paper material that increases the surface area for trapping particles. They generally have MERV ratings from 8 에게 13. These filters capture a wider range of particle sizes, including mold spores and pet dander. Their denser material improves filtration without significantly reducing airflow, making them a popular choice for homes and offices.
3. Electrostatic Filters
Electrostatic filters use static electricity to attract and hold airborne particles. They can be either washable or disposable. Their MERV ratings vary widely, often between 8 그리고 13. While they can capture small particles effectively, their performance depends on the static charge, which may weaken over time or with washing.
4. HEPA 필터
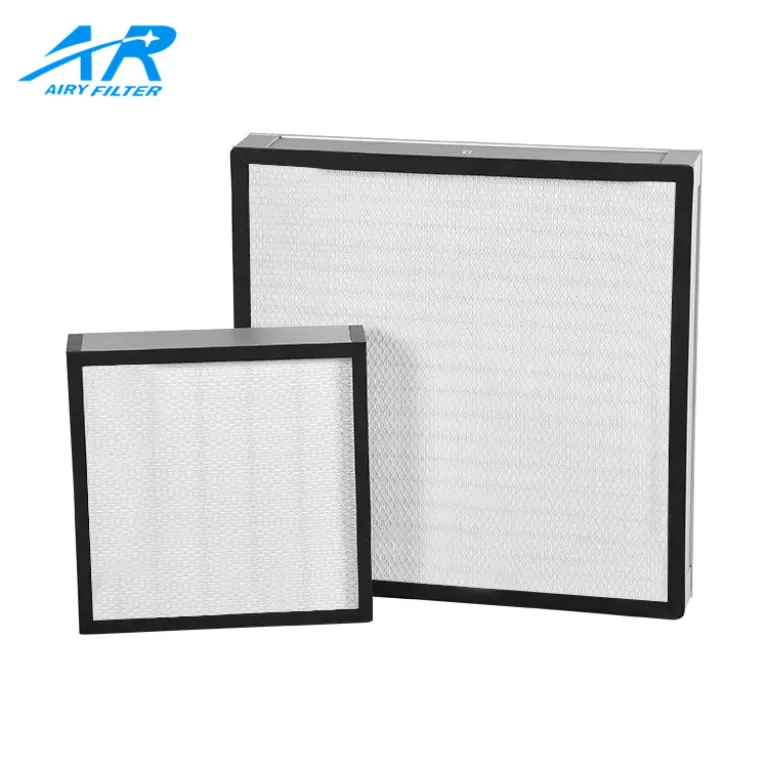

고효율 미립자 공기 (헤파) 필터 are designed to capture at least 99.97% of particles down to 0.3 미크론. These are used in environments requiring very clean air, 병원과 같은, 실험실, 그리고 깨끗한 방. HEPA filters have very high filtration efficiency but also cause high airflow resistance. HVAC systems need to be specifically designed or upgraded to handle HEPA filters.
5. 활성화 된 탄소 필터
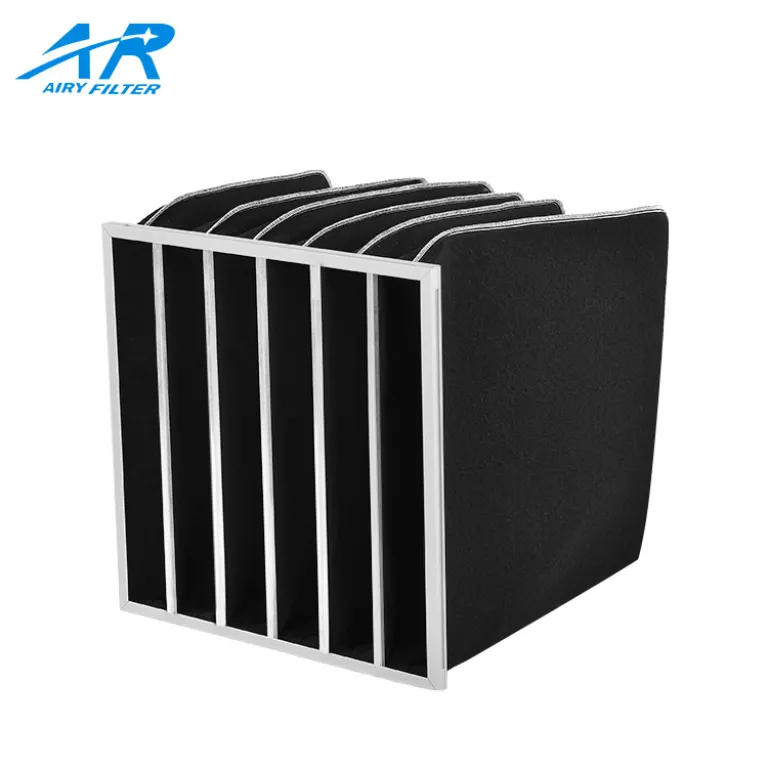

활성탄 필터 are primarily used to remove odors, 가스, 및 휘발성 유기 화합물 (voc). They do this by adsorbing these substances onto the porous surface of activated carbon. These filters are often combined with other types like pleated or HEPA filters to provide both particle and gas filtration.
5. 활성화 된 탄소 필터

Paint booth filters are specially designed to capture overspray particles, 먼지, and contaminants during painting processes. This type of air filters typically made from fiberglass, polyester, or synthetic media. Also these filters can be divided into four types: intake filters, exhaust filters, air makeup filters, and specialty filters.
Read more: 다른 유형의 페인트 부스 필터는 무엇입니까??
| 에어 필터 유형 | Material | Typical MERV Rating | 프로 | 단점 | Application |
| Fiberglass Filters | Layered fiberglass fibers | 1 – 4 | Low cost Minimal airflow resistance Protects HVAC components | Low filtration efficiency Not effective for small particles Frequent replacement | Basic HVAC protection, residential use |
| 주름 필터 | Folded fabric or paper | 8 – 13 | Better filtration than fiberglass Captures mold spores and pet dander Reasonable airflow | Higher cost than fiberglass Needs regular replacement Not for very fine particles | 주택, 부엌, 상업용 건물 |
| Electrostatic Filters | Electrically charged synthetic fibers | 8 – 13 | Washable and reusable Effective for small particle Moderate cost | Performance drops as static weakens Requires cleaning Filtration less consistent | Residential and light commercial use |
| HEPA 필터 | Dense mat of randomly arranged fibers | Above 13 (not standard MERV) | Extremely high filtration efficiency Captures bacteria and viruses Ideal for sensitive environments | High airflow resistance Expensive Requires specialized HVAC systems | 병원, 실험실, 깨끗한 방, critical environments |
| 활성화 된 탄소 필터 | Porous activated carbon | N/A | Removes odors and chemical pollutants Can combine with particle filters | Does not remove particulate matter Limited lifespan Frequent replacement needed | Odor control in homes, industrial air purification |
| 페인트 부스 필터 | 유리섬유, polyester, synthetic media | 다양합니다; often not rated by MERV | Effectively traps paint overspray and contaminants Maintains clean painting environment Multiple design options | Frequent replacement needed Can increase airflow resistance if clogged Higher cost than standard filters | Automotive paint booths, industrial spray painting, furniture manufacturing |
How to Choose Between Different Types of Air Filter?
Selecting the right air filter requires balancing several factors: 여과 효율, airflow resistance, 비용, and application environment.
- Understand Your Needs: 예를 들어, a standard office might only need a pleated filter with a MERV 8 에게 11 rating. In contrast, medical or industrial spaces might require HEPA filtration.
- Consider HVAC Compatibility: Not all HVAC systems can handle filters with high MERV ratings. A filter too dense can reduce airflow, leading to higher energy costs and system wear.
- Evaluate Indoor Air Quality Concerns: If odors or VOCs are a problem, activated carbon filters are beneficial. For allergy sufferers, filters that capture smaller particles (Merv 11 이상) are better.
- Budget and Maintenance: Fiberglass filters are cheap but need frequent replacement. Pleated and electrostatic filters offer better value over time. HEPA 필터, while expensive, provide unmatched air cleanliness but have higher maintenance and installation costs.
Tips for Maintaining and Replacing Your Air Filter Effectively
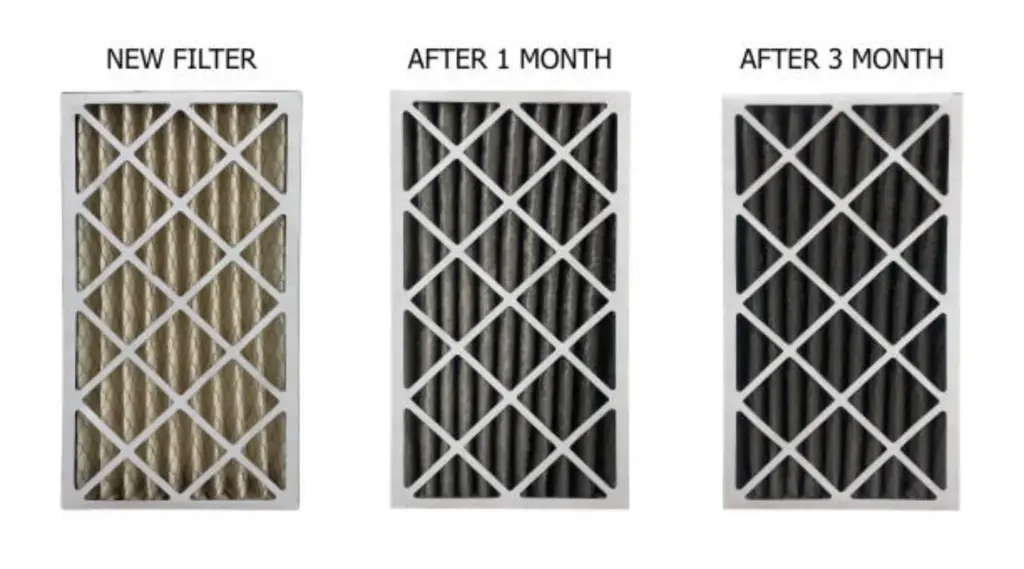

Proper maintenance is crucial for maximizing your air filter’s effectiveness and lifespan.
- Check Filters Regularly: Inspect your filter every month, especially during high usage seasons like summer and winter.
- Replace on Schedule: Follow manufacturer recommendations, typically every 3 주름진 필터의 경우 개월. Electrostatic washable filters should be cleaned regularly according to instructions.
- Keep Spare Filters: Having replacements on hand prevents system downtime and ensures consistent air quality.
- Maintain HVAC System: A clean HVAC system reduces dust buildup and improves filter performance. Regular professional servicing is advisable.
- Monitor Air Quality: Using air quality monitors can help you determine when filters need replacement or upgrade.

~에 통풍이 잘되는 필터, a dedicated air filter manufacturer, we recommend evaluating your specific environment and air quality goals before selecting a air filter type. If you require guidance or customized filtration solutions, our technical experts are available to assist with product selection and application support. No further than us today!